Hey guys, what’s up? Today we’re going to talk a bit about HTML SEO tags and how they impact on SEO and content creation strategies.
We know that it is very important to consider aspects that go beyond a good text, with beautiful images and original ideas.
In this article, we’re going to talk about what they are, what they’re for, where they live and what they eat! Jokes aside, even if you don’t know much about technical SEO, feel free to read on because everything has already been translated 😉
HTML SEO tags: what are they? What are they for?
Just as we talk to each other, we also need to “talk” to the algorithms responsible for distributing content on the web. This happens through HTML tags, the “language of computers”.
HTML tags are lines of code, usually used by programmers, to describe the structure of content to search engines, define the subjects your site is about and how to rank it.
So we can use these tags to emphasize and highlight essential elements of the content, as well as describe images and instruct search engine bots on how they should “read” the posts.
But it doesn’t stop there! HTML tags can also have a major influence on how pages appear in the SERP (Search Engine Results Page), i.e. Google’s results pages, for example.
By using them correctly, it is possible to transform ordinary search snippets into rich snippets, which have more attractive elements and usually have great results for content production.
Types of HTML tags
Now let’s understand what the types of HTML tags are and how each one will contribute to improving your SEO strategy!
Some of them may be known by more than one name, so I’ll put the most common ones here so you don’t get lost, okay?
Title tag or SEO title
It’s the title that appears in Google searches. As it is the part with which the reader usually has first contact, the title tag has a direct impact on ranking.
It usually directs the user to the content and is very visible:
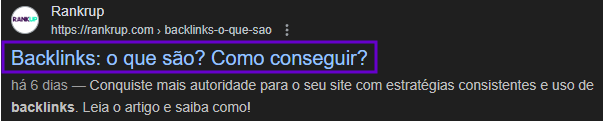
As Google uses semantic search, in which the entire context is taken into account, it is possible that you will find a different title in the search than the one you defined. Why does this happen?
Some time ago, search engines used very superficial criteria for ranking. One of them was the number of repetitions of the keyword. The bad thing about this is that content was often produced with a very large number of repetitions with the sole focus on achieving a good position. In this way, the user experience was compromised.
Today we know that the experience is much more important, that the focus is on engaging the reader and keeping them on the page for as long as possible.
This way, you can rank on the first page for a subject that is in the middle of your text. This is because search engines understand that that part of the content answers the user’s question objectively and completely.
Meta description
The meta description is, as the name implies, a brief description of the content you will find in the text. You can use copywriting techniques and CTAs (call-to-actions) to attract the user’s attention and convince them to visit the page.
It is also a visible tag, which you can see like this:
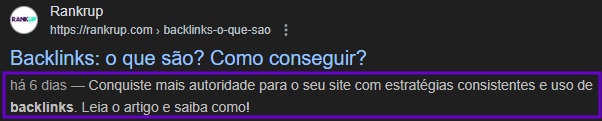
Although not a direct ranking factor, an attractive meta description generates more clicks. This can make Google understand that your content is relevant and deserves a better ranking position.
As search engines are focused on the user, you may also find a different meta description to what you wrote. Google search analyst John Mueller explains that there are several adjustments until the final result appears on the SERP.
This way, different users can find different meta descriptions for the same content, which improves the relevance of the content.
Do your bit
Although there are a number of search engine refinement mechanisms, it is essential that you do your bit! A good proportion of original descriptions are displayed in the SERP.
There are a few criteria you can follow to improve your results:
- Avoid click-baits and sensational headlines that have nothing to do with the text;
- Keep the length of the meta description to 160 characters;
- Use calls to action to persuade the reader to click on your text;
- Use more than one keyword (if it makes sense);
- Use keywords at the beginning of the text.
Titles, heading tags or header tags
Headings are used to organize and divide content into sections or chapters. This helps hierarchize the information, resulting in more organized and coherent material. They are divided into h1, h2, h3, h4, h5 and h6.
In addition, the division into headings and subheadings helps the reader to identify what the topic of that particular paragraph is about, making the experience more enjoyable and the reading more fluid. You can see it on the page like this:
How to organize heading tags on the page
It is recommended to use only one h1 per page, and it is also important that it contains the keyword you want to rank for right from the start.
As well as making it easier for the user to navigate through the content, titles contribute to the indexing of passages, which I’ve talked about before, remember?
Google then uses sections of the page as a separate search result, taking the user to the answer they are looking for more quickly.
H1 is the main title of the page, different from the title tag that appears in search results. There is no character limit for H1, allowing greater flexibility compared to the title tag.
H2 headings are used to divide content into chapters, H3 to subdivide into subchapters, and so on up to H6, which is usually used in very long articles on more complex subjects.
Another interesting possibility is that Google can use the titles as a list in the snippet to give the user a quicker response, as in this example:
When we look inside the text, there is no such result. Take a look:
That’s why it’s important (whenever possible) to have titles with similar sizes.
Alternative attribute (Alt tags)
The alternative text attribute is basically text that describes an image. It thus contributes to accessibility, i.e. it is the text that a reader finds to describe something to a visually impaired person, for example.
Likewise, it is the text that appears if the image does not load, making it easier for the user to understand, even if the visual resource is not available.
This also makes it easier for search engines to find images , as it helps to increase the ranking of images in Google searches. Therefore, even though AIs can read images, offering a detailed description makes this process easier 😉
Tag robots
The robots tag is a code in the HTML that makes a selection of pages that will be indexed. It does a similar job to robots.txt, however, robots.txt can also suggest some things.
But why is this important since the intention is to index as many pages as possible? 🤔 The real question is which ones you don’t want Google to index for security or privacy reasons.
So it’s not a good idea for lots of people to have easy access to your website’s login page, for example. Or even to confidential documents that may be stored there.
In this case, just add a noindex tag for this page.
Learn some of the parameters of the robots tag
Google understands and respects the following parameters in its robots tag:
Noindex – prevents search engines from indexing a page;
Nofollow – prevents the search engine from following all the links on the page (this is why it is different from the nofollow attribute which is applied at an individual URL level);
Follow – the links on the page must be followed even if the page is not indexed;
Noimageindex – the images on this page will not be indexed;
Noarchive – prevents a cached copy of the page from appearing in the search results;
None – the same as “noindex, nofollow”.
Canonical tags, canonical mark, canonical tag
If you have two pages with similar content, you can use a canonical tag to tell search engines which one to prioritize.
It thus avoids problems of duplicate content on your site. In this sense, the canonical tag also avoids cannibalization, when texts compete with each other in search results, which reduces your chances of ranking.
How do I know if the HTML tags on my page are correct?
Google can read tags in HTML and XHTML. So, for those of you who are curious about this, there are a few ways to see how the tags are arranged in the code.
One of the easiest ways to view HTML tags is to go straight to the page’s source code. You can do this in a few ways:
- Right-click on an area of the page and then click on “View page source code”;
- In Google Chrome, you can select the Ctrl+U command. Once the code appears, you can use Ctrl+F to search for “<meta or <title”.
Google Search Console frequently scans your site and flags improvements that Google’s robots have found. That’s why it’s important to do a thorough job of following up.
If you use a Content Management System (CMS), such as WordPress, for example, you don’t have to worry about inserting the tags manually!
Follow the recommendations above in this article and you’ll get great results.
However, if you want to dig deeper and see for yourself, here’s a Google page that goes into more detail about the attributes of HTML tags.
Conclusion
In short, HTML SEO tags are powerful tools for communicating with search algorithms and are fundamental to a site’s positioning in the SERP.
They play a crucial role in structuring content, describing images and instructing bots how to interpret pages.
In addition, they directly influence the user experience and the relevance of the content, essential factors for a good ranking.
It is therefore essential to understand and apply these tags correctly to ensure that your content not only reaches your target audience, but also offers a rich and engaging experience.
Remember that, despite advances in algorithms, the human part of SEO optimization is irreplaceable and remains the key to success on the web. See you next time! 😉